Bank of Canada Holds Policy Rate Steady Amid Global Uncertainty
 It is rare for the Bank of Canada and the US Federal Reserve to announce rate decisions on the same day, but today’s announcements highlight the stark differences in policy in the two countries. The Bank this morning announced they would maintain their target for the overnight rate at 1.75% for the eighth straight meeting. The Fed is widely expected to cut its target for the fed funds rate by another 25 basis points, taking it below the key rate in Canada for the first time since 2016. More than 30 central banks have cut interest rates in the past year and the Bank of Canada in today’s Policy Statement highlighted the weakening in the global economic outlook since the release of its July Monetary Policy Report (MPR).
It is rare for the Bank of Canada and the US Federal Reserve to announce rate decisions on the same day, but today’s announcements highlight the stark differences in policy in the two countries. The Bank this morning announced they would maintain their target for the overnight rate at 1.75% for the eighth straight meeting. The Fed is widely expected to cut its target for the fed funds rate by another 25 basis points, taking it below the key rate in Canada for the first time since 2016. More than 30 central banks have cut interest rates in the past year and the Bank of Canada in today’s Policy Statement highlighted the weakening in the global economic outlook since the release of its July Monetary Policy Report (MPR).
In today’s MPR, the Bank revised down its forecast for global economic growth this year to below 3.0%, reflecting a downward revision in growth in the United States to 2.3% (from 2.5%), the Euro area (to 1.1% from 1.2%), oil-importing emerging market economies and the rest of the world. China’s growth pace remains at a 30-year low of 6.1%.
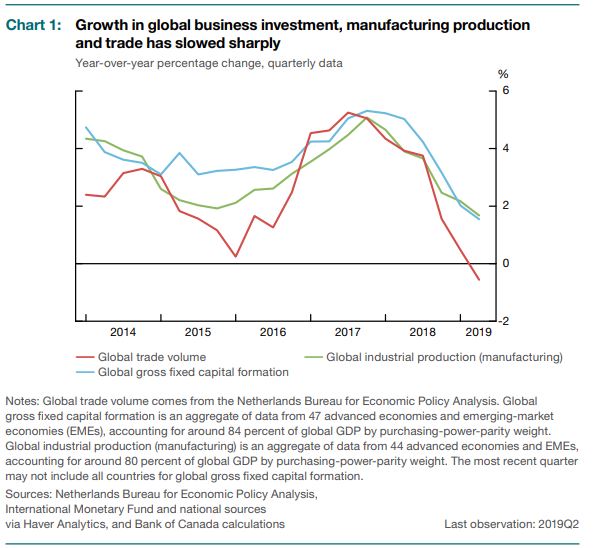
Trade conflicts and uncertainty are weakening the world economy to its slowest pace since the 2007-09 economic and financial crisis. The slowdown has been most pronounced in business investment and the manufacturing sector and has coincided with a contraction in global trade (Chart 1). Despite the manufacturing slowdown, unemployment rates continue to be near historic lows in many advanced economies, as growth in employment in service sectors has remained resilient.
Growth is projected to strengthen modestly to around 3.25% by 2021, with a pickup in some emerging-market economies (EMEs) more than offsetting slower growth in the United States and China.
Canada has not been immune to these developments. Commodity prices have fallen amid concerns about global demand. Despite this, the Canada-US exchange rate is still near its July level, and the Canadian dollar has strengthened against other currencies.
Growth in Canada is expected to slow in the second half of this year to a rate below its potential. This reflects the uncertainty associated with trade conflicts, the continuing adjustment in the energy sector, and the unwinding of temporary factors that boosted growth in the second quarter. Business investment and exports are likely to contract before expanding again in 2020 and 2021. At the same time, government spending and lower borrowing rates are supporting domestic demand, and activity in the services sector remains robust. Employment is showing continuing strength and wage growth is picking up, although with some variation among regions. Consumer spending has been choppy but will be supported by solid income growth. Meanwhile, housing activity is picking up in most markets. The Bank continues to monitor the evolution of financial vulnerabilities in light of lower mortgage rates and past changes to housing market policies.
Canadian Economy Boosted By Housing
The Canadian economy grew at a moderate pace over the past year, supported by a healthy labour market and the recent turnaround in housing. However, global trade conflicts and related uncertainty dampened business investment and export activities, and investment in the energy sector continued to decline. The impact on growth of both global headwinds and energy transportation constraints is expected to diminish, and the pace of economic expansion should gradually pick up in 2020 and 2021.
In 2020 and 2021, Canada’s economy is anticipated to grow near potential. Consumer spending is projected to increase at a steady pace, and housing activity to continue its ongoing recovery. Overall, investment and exports are anticipated to grow moderately. In the energy sector, investment is forecast to stabilize, and oil exports should improve as pipeline and rail capacity gradually expands.
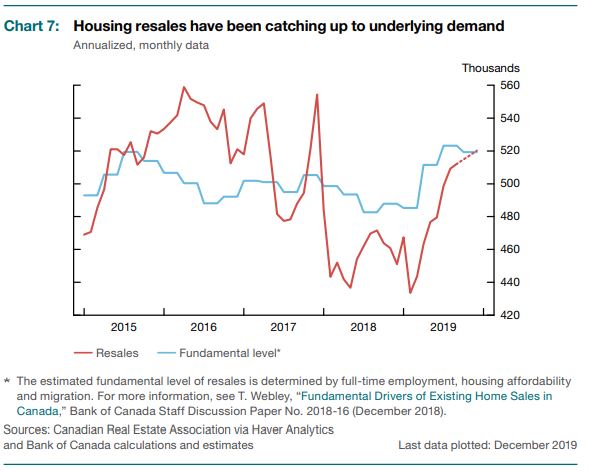
In today’s MPR, the Bank states that housing resales have been catching up to underlying demand (see chart 7 from the MPR). Housing markets generally reflect regional economic conditions. Housing starts and resales have been particularly robust in Quebec and Ontario, where labour markets have been strong. These provinces will likely continue to be the main drivers of the growth in residential investment. In Alberta, where the oil industry is expected to stabilize, modest improvements in housing are expected. In British Columbia, residential investment has recovered in recent months and should remain near current levels, reflecting the creation of new households.
Bottom Line
The dovish tone of today’s policy statement suggests that the Bank of Canada has become more cautious in its holding pattern amid a weakening global economy. The central bank “is mindful that the resilience of Canada’s economy will be increasingly tested as trade conflicts and uncertainty persist,” policymakers led by Governor Stephen Poloz said in the statement. “In considering the appropriate path for monetary policy, the Bank will be monitoring the extent to which the global slowdown spreads beyond manufacturing and investment.”
The statement and the fresh batch of more pessimistic growth forecasts will raise questions about the central bank’s commitment to a neutral stance on rates, particularly in the face of global easing in many other countries that has made the Bank of Canada an outlier. If the Federal Reserve lowers its interest rates later today, as expected, the Bank of Canada would have the highest policy rate in the industrialized world.
It may well be that the Bank of Canada cuts rates early next year. Mitigating this prospect is that the Bank was more bullish on consumption and housing–fueled by the robust labour market. Another source of future growth is additional fiscal stimulus from Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s newly elected Liberal government, which has promised to implement new spending and tax cuts next year. For now, the Bank is maintaining a neutral stance.